Mila Grieg, MD
Executive Medical Director,
Therapeutic Area Medical Lead

Autoimmune diseases often involve overlapping mechanisms and diverse symptoms, making clinical research particularly challenging. Our role as an Immunology and Inflammation CRO involves designing and executing studies that accurately capture these complexities. We have successfully conducted trials across various indications, including rheumatology, dermatology, and gastrointestinal autoimmune disorders.

Our Immunology & Inflammation ACE is a dedicated hub of therapeutic, operational, and scientific expertise designed to accelerate your success in inflammation and immunology clinical trials. Staffed by cross-functional leaders in autoimmune, allergic, and inflammatory diseases, the Immunology & Inflammation ACE drives innovation in trial design, endpoint strategy, biomarker integration, and patient engagement. We bring deep knowledge, nimble execution, and lessons learned from hundreds of inflammation and immunology clinical trials. Whether you’re launching a first-in-human trial or scaling for global Phase III, our ACE ensures consistency, quality, and agility at every step.
Strategic, adaptive, and indication-specific trial designs for Immunology & Inflammation success.
We develop scientifically sound and operationally feasible protocols tailored to the complexities of immunology and inflammation indications. From Phase I to Phase III, our designs incorporate adaptive elements, targeted eligibility, and real-world feasibility to accelerate timelines, minimize amendments, and optimize data capture. Our team ensures that every trial starts with the right foundation to reduce risk and enhance execution.
Meaningful endpoints aligned with disease variability and regulatory expectations.
Choosing the right endpoints in Autoimmune clinical trials is critical, especially with diseases that present heterogeneously. We combine clinical insight, regulatory intelligence, and statistical expertise to define primary and secondary endpoints that are designed to provide a true and meaningful assessment of efficacy and support regulatory success. Whether using traditional, composite, or patient-reported outcomes, we ensure endpoints are measurable, relevant, and capable of capturing meaningful change.
Seamless biomarker strategy from discovery to validation.
Biomarkers play a vital role in patient stratification, efficacy assessment, and regulatory differentiation. Our Center of Excellence helps biotechs design and implement integrated biomarker plans—from selecting appropriate assays and central labs to interpreting results and aligning with clinical outcomes. We bridge the gap between translational science and clinical execution, ensuring biomarkers deliver actionable insights and regulatory value.
Proactive, patient-centric strategies that enhance trial participation and retention.
Long-duration inflammation and immunology clinical trials require more than recruitment—they demand sustained engagement. We design retention strategies that anticipate patient needs, reduce burden, and support adherence. From digital tools and home health services to flexible visit scheduling and travel support, our approach improves patient experience and boosts data continuity and compliance. Engaged patients are retained patients, and we make that happen—thoughtfully and nimbly.

Clinical trials in immunology and inflammation are among the most complex in the industry—marked by competitive landscapes, variable disease expression, evolving endpoints, and long timelines. For emerging biotechs, these obstacles can slow progress and increase risk. That’s where we come in. Backed by deep therapeutic expertise and a nimble, full-service model, we help you anticipate issues, adapt quickly, and move forward with confidence. Below are the top challenges biotechs face—and how we solve them.
Learn More

Biotechs advancing immunology and inflammation assets face regulatory uncertainty, especially when working with novel modalities or biomarkers in early-phase trials. With varying global expectations and constant updates in FDA/EMA guidance, many struggle to define the right development path. Allucent offers deep regulatory expertise and early scientific engagement with regulators. We help refine your strategy, align endpoints with expectations, and craft compelling briefing documents. This proactive approach de-risks early development, speeds up approvals, and avoids costly protocol amendments—setting your asset up for long-term success across key markets.
Learn More
Autoimmune and inflammatory trials often target the same limited patient populations, leading to competition for sites and subjects. Diseases like IBD, RA, and lupus require not just speed, but precision in recruitment. We mitigate these risks through advanced feasibility modeling, AI-driven site matching, and partnerships with community practices and academic centers. Our teams implement pre-screening tools and patient concierge services to reduce dropout and improve retention. The result: faster, more predictable enrollment, even in saturated markets where many studies compete for the same patient populations, sites, or indications.
Learn More

In Immunology & Inflammation, disease expression varies significantly by patient, making it difficult to choose endpoints that are both clinically meaningful and statistically powerful. Trial failure often results from inadequate endpoint sensitivity or poor biomarker validation. Our biostatistics, clinical pharmacology, and data science experts collaborate early in trial design to select validated or novel endpoints tailored to disease complexity. We also use advanced modeling and simulations to fine-tune protocol considerations, enabling adaptive trial strategies that increase confidence in go/no-go decisions, understanding probability of success and ultimately improve development outcomes.
Learn More

Emerging biotechs are often lean, with limited bandwidth to manage the operational and scientific demands of inflammation and immunology clinical trials. This leads to delays, quality issues, or missed insights. We act as a true extension of your team—offering flexible partnership models, cross-functional leadership, and seamless integration across strategy, operations, and science. Our therapeutic-area experts bring deep domain expertise to elevate every decision point, while our full-service capabilities scale with you from first-in-human to Phase III. With us, you’re not just outsourcing work—you’re gaining a committed ally invested in your success.
Learn More

Chronic Immunology & Inflammation diseases often require long-duration trials, increasing dropout risks and raising costs. Keeping patients engaged and compliant becomes a significant hurdle, especially when using invasive procedures or long-term assessments. We deploy patient-centric retention strategies, including digital engagement tools, home health support, and travel logistics. Our data monitoring systems proactively flag disengagement risks, allowing intervention before dropout occurs. With our approach, you gain higher data completeness, reduced protocol deviations, and better long-term compliance—essential for maintaining study power and meeting endpoints.
Learn More
Selecting the right immunology CRO is crucial for the success of your clinical trial. Allucent has executed studies for autoimmune treatments across a wide variety of indications:
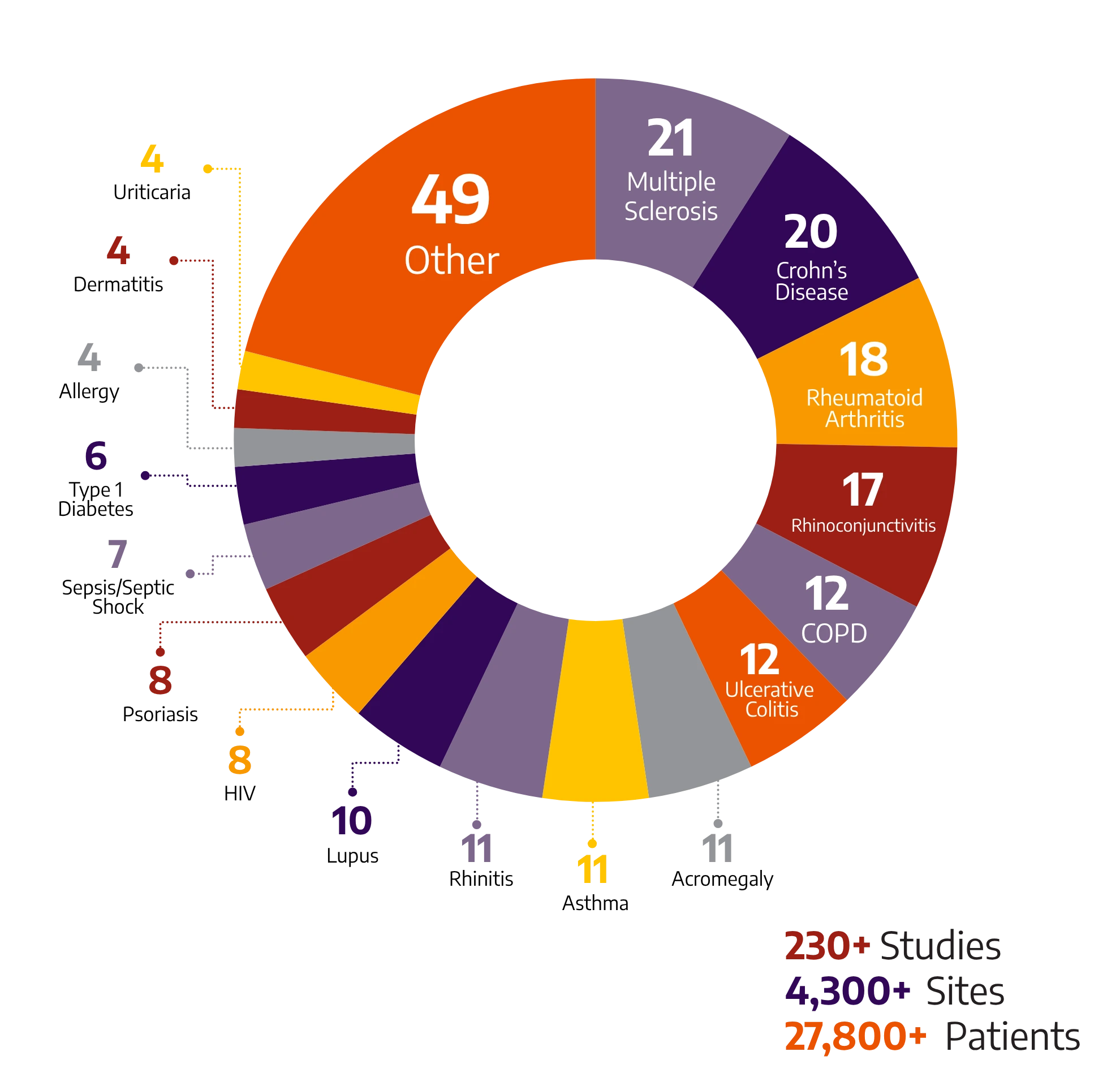
Our extensive experience as an inflammation CRO enables us to tailor our approach to each unique study, ensuring optimal outcomes.
Allucent understands the varied manifestations of lupus. Our team has experience in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), lupus nephritis, and cutaneous lupus erythematosus. With 14 completed studies spanning Phases I-III, our expertise as an immunology CRO ensures that trials are designed and conducted with precision.
Autoimmune conditions affecting connective tissues present unique challenges due to symptom variability. It takes deep experience to manage rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials effectively. As an inflammation CRO, we offer expertise in managing studies for conditions like SLE, psoriatic arthritis, and scleroderma.

Autoimmune conditions readily and regularly impact the dermis, but in ways that pose challenges in diagnosing and isolating an appropriate sample population. Our expertise as an immunology CRO extends to psoriasis and various forms of dermatitis, including deep experience in both psoriasis clinical trials and atopic dermatitis clinical trials. We understand the complexities of enrolling and retaining patients with fluctuating disease severity and treatment histories, and we bring proven capabilities in endpoint selection, digital imaging, and investigator training tailored to dermatologic studies. From topical agents to biologics, our teams support every phase of development to ensure scientifically rigorous and patient-centric execution.
The intersection of hematological and autoimmune disorders involves complex mechanisms Our role as an immunology CRO includes conducting studies on autoimmune hemolytic anemia, sickle cell disease, TTP, and more, with a focus on isolating and understanding overlapping disease processes.
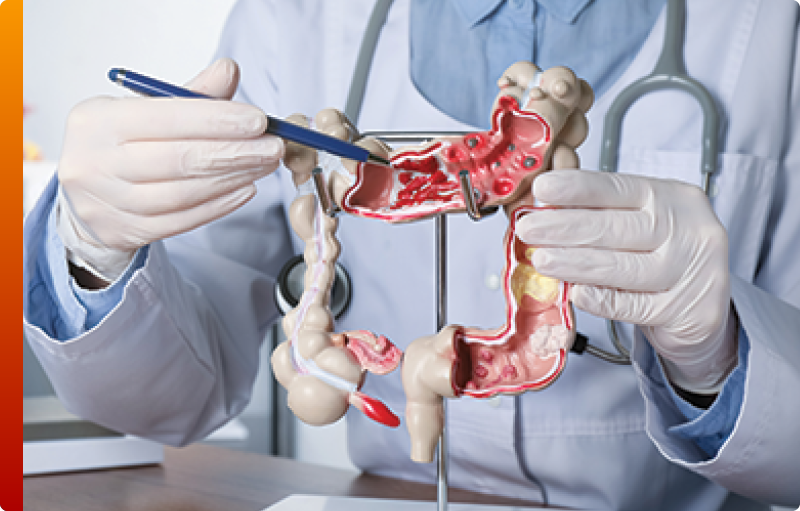
Gastrointestinal autoimmune disorders can manifest in a variety of ways—from oral ulcers to diarrhea, bloating to abdominal pain. Our immunology CRO experience spans the full spectrum of inflammatory bowel disease clinical trials, including deep expertise in both Crohn’s disease clinical trials and ulcerative colitis clinical trials. We understand the diagnostic and operational complexities these studies present and are equipped to design and execute trials that deliver meaningful, actionable outcomes. Whether supporting early-phase studies or large, late-stage programs, our team brings the scientific insight and operational precision needed to advance therapies for IBD and related gastric conditions.


Let us know how we can help you bring new therapies to light. Get in touch to get started.
Want to help small and mid-size biopharma companies change the therapeutic landscape?