Autoimmune and Inflammation
Our experts can bring essential insights to autoimmune disorder trials across a variety of indications

We address the specific challenges of multiple mechanisms and varied symptoms in autoimmune and inflammation trials.
The complexity of autoimmune disorders means understanding these diseases and their potential treatments more deeply. We look forward to working side-by-side with you as you offer new hope to the patients who suffer from these perplexing conditions.
Our expert teams have conducted autoimmune clinical trials in numerous disease states, from the divergent symptoms of rheumatology to the wide-ranging conditions resulting from gastrointestinal autoimmune disorders.
We’ve worked on trials requiring us to understand and isolate the overlapping mechanisms in autoimmune and hematological disorders. We’ve successfully identified the correct patient populations for dermatological autoimmune studies. And we’ve honed our systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) expertise by completing 14 studies involving this disease.
Wide-Ranging Autoimmune Experience
Choosing a team with the right kind of therapeutic experience for your clinical trial is essential. Our teams have executed studies for autoimmune treatments across a wide variety of indications:
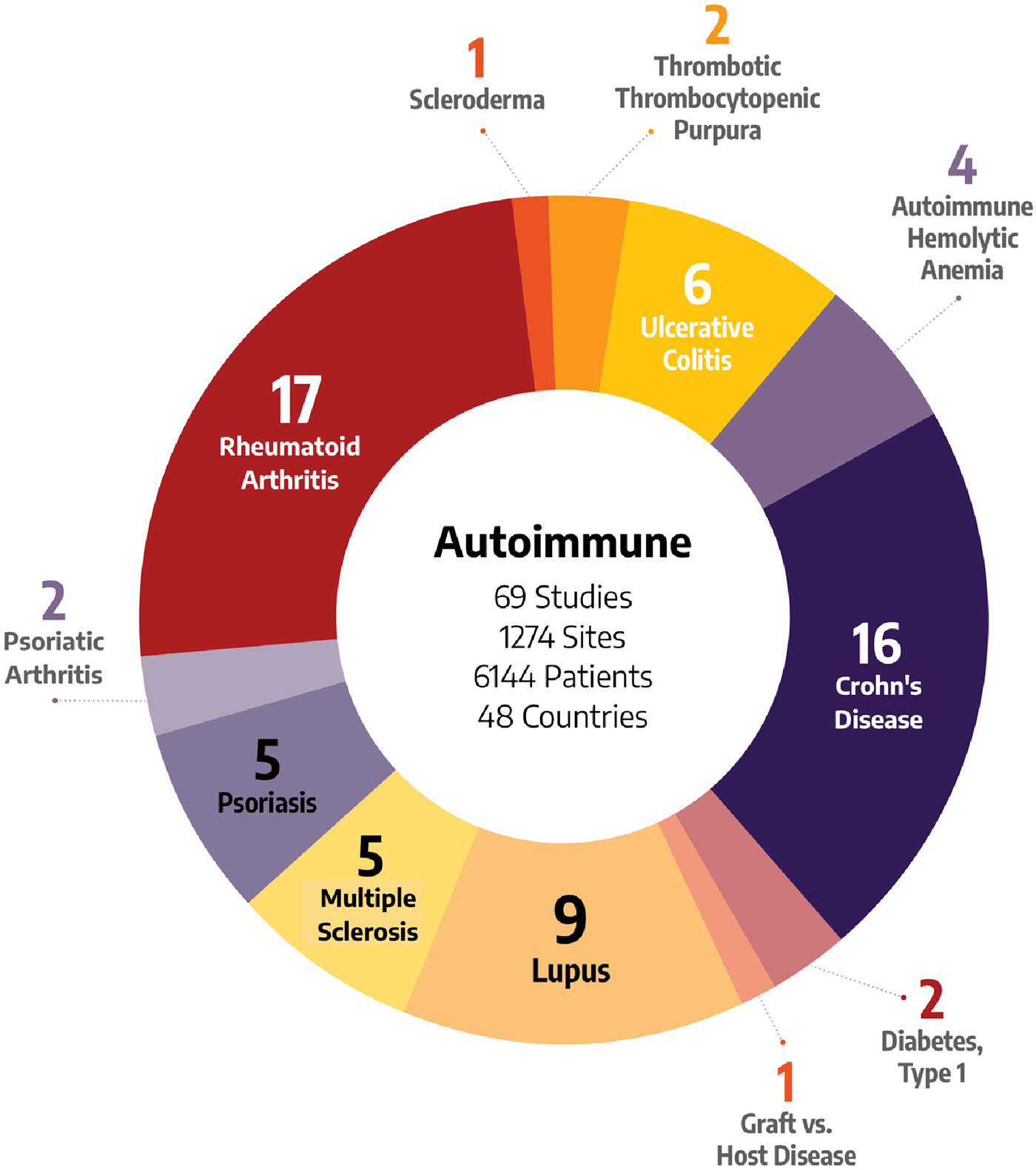
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
- Crohn’s Disease
- Dermatitis
- Diabetes, Type I
- Graft vs Host Disease
- Lupus (SLE & Nephritis)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Scleroderma
- TTP (Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura)
- Ulcerative Colitis
Experts in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Clinical Trials
Allucent understands how lupus can manifest differently. Our team has experience in SLE as well as lupus nephritis and cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Our experience in lupus runs deep, with 14 completed studies spanning Phases I-III.
Extensive Autoimmune Clinical Trial Expertise
RHEUMATOLOGY
The impact of autoimmune conditions on connective tissues is relatively common, but this area of study is also challenging because symptoms can vary widely. It takes experience to manage this effectively in a research study environment. We offer expertise in SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, and scleroderma.

DERMATOLOGICAL AUTOIMMUNE
Autoimmune conditions readily and regularly impact the dermis, but in ways that pose challenges in diagnosing and isolating an appropriate sample population. Our expertise extends to psoriasis and various forms of dermatitis.
AUTOIMMUNE AND HEMATOLOGY
In hematology and autoimmune disorders, there can be several mechanisms present. From marrow to red blood cells and platelets, various manifestations are possible. Our expertise includes autoimmune hemolytic anemia, sickle cell, TTP, and more.
GASTROINTESTINAL AUTOIMMUNE
Gastrointestinal autoimmune disorders can manifest in a variety of ways, from oral ulcers to diarrhea, bloating to abdominal pain. Our experience helps us determine morbidity and conduct studies that yield actionable results, with strengths in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, among others.
